CCHE2D/3D Sediment Transport Model
Key capabilities
|

|
|
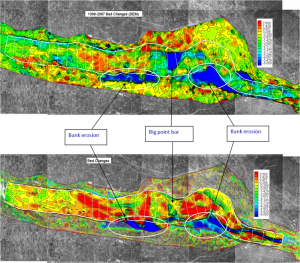
Bank Erosion of Chuoshui Creek Chuoshui Creek is a mountain river in Taiwan characterized by a steep slope, an abundant supply of sediment and a high rate of precipitation in typhoon seasons. The river has a braided channel pattern with rapidly changing sub-channels. Both bed erosion and bank erosion are significant, particularly during the typhoon seasons, resulting in fast channel changes and a severe farmland loss along the banks. The CCHE2D sediment transport and bank erosion model was applied to simulate the sediment transport and morphodynamic processes in one reach of the river.
|
|
|
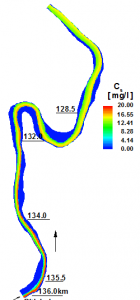
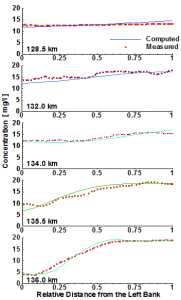
CCHE2D -SED has been applied to simulate suspended sediment transport in a natural river. The sediments mainly come from a branch channel of the right bank. Comparisons of the simulated results and observation in multiple transacts show good agreements of total sediment concentration and the lateral redisbution. |
|
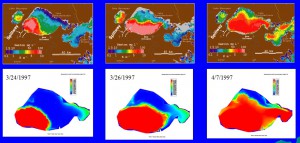
Comparisons of CCHE2D simulated sediment transport in Lake Pontchartrain, LA, after the 1997 flood release from the Mississippi River to the lake. The simulated distributions of suspended sediment are very close to those observed with satellite imagery.
|
|
|
|
|
|
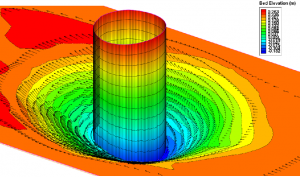
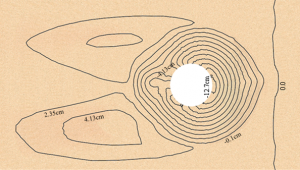
CCHE3D has been applied to simulate local scouring around bridge piers and obtained good results. The scour depth and shape of the scour hole agreed well with multiple sets of physical experimental data. |