CCHE2D/3D Flow Models
Key capabilities
|
|
|
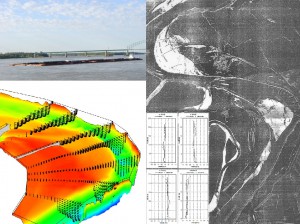
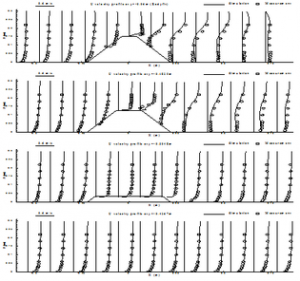
Three-Dimensional Model Validated by Field Data
Large rivers can be used for navigation. The secondary helical flows, however, often make it difficult for commercial barges to maneuver through the bendways of river channels. CCHE3D has been used to simulate complex flows in bendways of the Mississippi River where submerged weirs were installed to modify the flow distribution and improve navigation conditions. The model has been used for evaluating the effectiveness of the installed structures.
|
|
|
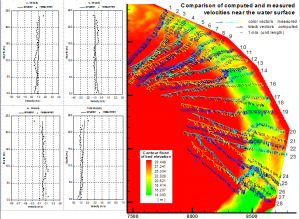
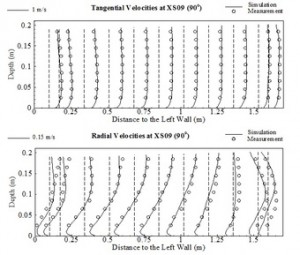
Validation of CCHE3D with Physical Model Data: A Submerged Dike
CCHE3D was validated using densely measured laboratory data (~2800 points) around a submerged spur dike. Excellent agreement between the simulation and the measured 3D velocity field was obtained.
|
|
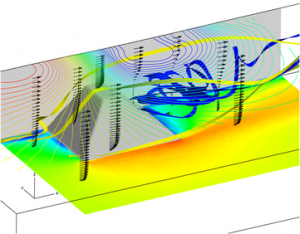
Validation of CCHE3D with Physical Model Data: A 180 Degree Channel Bend
Secondary currents in curved channels affect processes of navigation, sediment transport, bank erosion and channel morphologic evolution. A small outer bank re-circulation is often observed in addition to the major helical cell. Simulating these flow distributions requires sophisticated turbulence closure schemes and the ability to handle irregular shaped channels. |
|
|
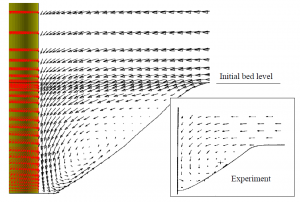
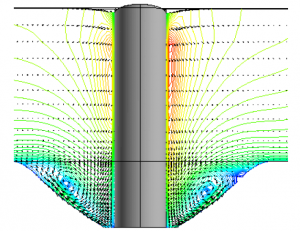
Scour holes around bridge piers in a natural river are caused by the turbulent flow around the pier. Scouring could result in bridge failure. Numerical study has been performed to simulate the horseshoe vortex by applying the CCHE3D model. Results of the simulation and the experimental data are in good agreement in these conditions
|
|
|
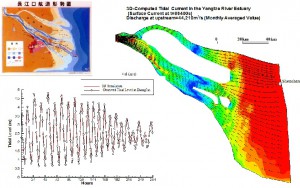
Simulated Fluvial Current and Tidal Wave Interaction in the Estuary of Yangtze River, China
Salinity intrusion is related to the dynamic balance of the river current, tidal wave and river estuary morphology. CCHE3D has been applied to the study of water quality study of the Yangtze River estuary. Accuracy of the 3D flow field is critical to this problem. |
|
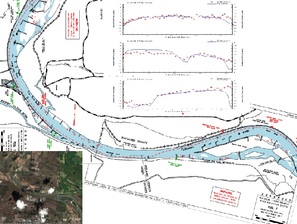
|
CCHE2D simulated flow in Arkansas River with numerous spur dikes. The project helps redesign the dike field for better navigation. The predicted the velocity distributions in the channel agreed very well with those measured. |
|
Simulated Unsteady Flows in a Dendritic Channel Network over a Watershed
Watersheds have complex topography, land-use, soil, rain and runoff distributions. Unsteady flow prediction in a channel network is important to understand other watershed processes. |
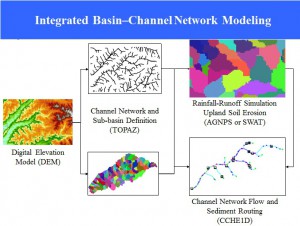
|
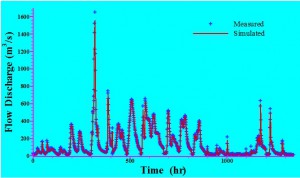
|